The relevance of this program is that it allows you to outline the guidelines for creating a holistic educational system, helps to make the pedagogical process purposeful, allows you to penetrate into the essence and mechanisms of upbringing.
In education there is no main and secondary, as there is no main petal among the many that create the beauty of the flower. In education, everything is important: the lesson, and the development of the versatile interests of children outside the lesson, and the relationships between the pupils among themselves and in the family.
Realizing this, at the very beginning of the academic year, the pedagogical staff at the expanded meeting of the methodical association of class leaders developed the following commandments in working with children:
1) Listen often to yourself: has the heart hardened, or does the teaching of the teacher fail?
2) the teacher is not the one who teaches, but who learns; first of all - a personal example in everything;
3) any business should be done as if it were your swan song. Do not repeat yourself, have your handwriting, boldly leave the templates, look for your cherished key to the heart of every child;
4) The barometer of any case is the child's eyes. To see in front of you is not a class, but a separate individual personality, unique, unique;
5) remember the principles of the three "no": DO NOT hurry, DO NOT harm, DO NOT blame children for your own mistakes and mistakes.
The school is the house where the future personality is being formed and how it is projected. And in this "designing" everything is important. That is why educational, pure learning activities are not enough. No matter how good, full-fledged, developing lessons were, some more additional tools are needed. Therefore, every teacher, every class teacher, in addition to the didactic system, creates an educational system connected with extracurricular work. Someone chooses as its core a civil-patriotic work, someone uses the basic principles of moral education, for someone an important role is played by tourism
In the "Conceptual framework for the content of the activities of the class teacher" it is said that the humanistic school realizes a real turn to the student's personality. It becomes really the subject of its development, and not the means by which teachers realize abstract plans and programs alienated from the individual.
This program is not designed for one year, but it is possible to make adjustments. The program represents a set of subprograms in various areas of educational work aimed at solving the tasks and containing the means for their implementation.
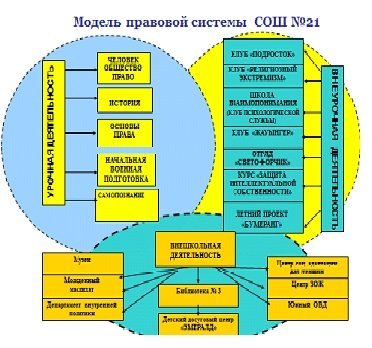
Structure of the school target comprehensive educational program
|
Direction of educational work. |
Subprogramme |
|
MORAL-INTELLECTUAL |
"ROAD TO YOURSELF" |
|
CIVIL-LEGAL,
PATRIOTIC |
"FROM LEGAL KNOWLEDGE -
TO THE CIVILIAN POSITION »
"PATRIOT" |
|
HEALTHY LIFESTYLE |
"HEALTHY LIFESTYLE
FROM THE TEACHER TO THE PUPIL |
|
PROFESSIONAL SELF-DETERMINATION |
" MY CHOICE" |
|
CHILDHOOD CORRUPTION |
"CENTER OF CHILDHOOD" |
|
ADDITIONAL EDUCATION |
Supplementary Education Development Program |
|
WORK WITH PARENTS |
"FAMILY AND SCHOOL TOGETHER" |
The concept of an educational system
with a description of its components
1. Actual questions
The system of education of the State Institution of Secondary School No. 21 reflects the humanistic direction in the educational activity of school teachers; takes into account the accomplished radical changes in the social life of the country; promotes the organization of upbringing as a factor in the adolescent's entry into the context of society.
The system of upbringing corresponds to the requirements of time and the socio-psychological situation that exists objectively in society. The grounds of the educational system of the school are:
- a pedagogical view of education from the standpoint of universal human culture;
- a pedagogical view of the components of the educational process as the assimilation, assimilation and appropriation of the world by the growing child entering this world;
- the definition of the content of the educational process as a system of relations to the values of a worthy life of a worthy person, and knowledge and skills as a means of the existence of human values to the world and the world;
The leitmotif of the school education system is the attitude towards the world: the schoolboy, together with the teacher, knows the world, interacts with the world, tries to love this world. Real, concrete, cruel, beautiful, understandable and incomprehensible world, full of problems that a person has to solve every minute (either himself, or using the proposed solution). And, by interacting with this ever more cognizable and comprehended world, the student acquires the ability to construct his life in a conscious and conscious way in accordance with this world. So or only so we can achieve a strategic goal: the formation of a personality capable of building a life worthy of Man
2. The purpose and objectives of the educational syst
Goal:
Bringing up a person who can be able to live a dignified life .
Tasks:
- Creation in the school of a single educational space of childhood, the main value of which is the personality of each child..
- The formation of consciousness, oriented to the ability to maintain respect for each other in any unfavorable conditions, to show concern, mutual understanding, aspiration for interaction.
3. The main types of joint activities of children and adults
1.Joint actions and operations conducted by teachers and students
2.Cultural-mass events according to the programs declared in the educational system
3.Monitoring results
4.The organization of self-government in school
5. Work of circles, sections, associations of additional education
6. Lectures for parents (according to the plan)
The types of activities announced for implementation will drive the chosen goals and content and give the necessary result with a gradual, step-by-step movement·
- Understanding and acceptance of the norms of cultural life. These norms are great, but all have a single basis - truth, good and beauty
- Formation of ideas about the person as the subject of life and the highest value on the Earth
- Finding a value attitude to the social structure of human life·
- The formation of a life position, the development of the ability to choose an individual's life path
The child's ascent to the values of culture, his movement from one step to another successfully passes only thanks to "accompaniment", the skilful management of the pedagogical process.
4. Subjects of the educational system
The educational system includes the following subjects:
- Classroom teacher.
-
The students themselves.
-
Parents (legal representatives).
-
Subject teachers.
-
School Administration
-
Psychologis
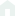
5. External links of the educational system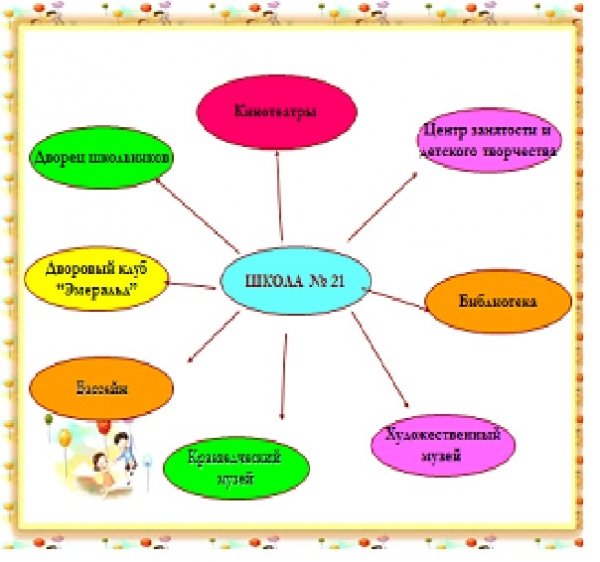
All the subjects of upbringing presented in their interrelation and interaction have an integral pedagogical influence on the intellectual, spiritual, moral and emotional-volitional sphere of the child. It is this that is the dominant idea of the integration of the constituent elements of the educational system.
A detailed description of ways to achieve goals educationalsystem
Stage 1
Purpose: to awaken creative activity among teachers, students, parents.
The main activities. Pedagogical conditions:
- study of opinions, interests of children, parents, teachers;
- study of society;
- selection and placement of personnel;
- organization of the work of groups of different profiles, clubs, sports sections, increasing the professional growth of teaching staff, creating the basis for creativity;
- mastering of new pedagogical technologies of influence on pupils.
II stage
Objective: to determine the strategy and tactics of development and improvement of the educational system (basic directions, forms and activities)
Tasks:
- improving the work of children's self-government bodies;
- continuation of traditions;
- Development in groups, classes, in each child of independence, initiative, responsibility, creativity.
The main activities. Pedagogical conditions:
- Clear planning as one of the most important prerequisites for the effectiveness of the educational system;
- educational work passes through all kinds and forms of activity;
- development of additional education: extracurricular work, additional courses; extra-hour creative activities, participation in district and regional programs;
- work in society with parents, community and sponsoring organizations;
- Creation of a unified educational process.
Stage III
The purpose: to provide qualitative results of educational and educational process in conditions of its variability and variety of pedagogical technologies
Objectives: creating a system of relationships that helps the student at each age stage successfully solve their tasks in the main fields of activity.
Pedagogical conditions
- Expanding the search innovative activity of teachers and the entire teaching staff in building new content and organizational and pedagogical models of education that stimulate the process of teaching and educating children in the interests of the development of the individual, family, village;
- Ensuring the continuity of educational and educational programs implemented in the chain of continuity of the younger, middle and senior levels.
Directions of the educational system
1. Extra-curricular and extracurricular work in the subjects of the humanities, mathematics, natural-geographical and other cycles (subject circles, intellectual competitions, olympiads).
2. Extracurricular and extracurricular work in the subjects of the artistic and aesthetic cycle. Realization of the tasks of artistic and aesthetic education and education of children, the work of circles and groups of music, educational, decorative and applied creativity, choreographic, theatrical direction, the holding of reviews, competitions.
3. Extracurricular and extracurricular sports work (sports clubs and sections, shows, competitions).
4. Extracurricular and extracurricular work on patriotic, legal, labor education (the program of associations, reviews, competitions, exhibitions, competitions).
5. Development of student self-government
6. Joint realization of leisure time for children and their parents (hikes, "Over a cup of tea", "Ogonki", competitions, exhibitions, intellectual games, trips and travel).
This "large-block" approach to the construction of educational activities helps in creating a school community. So the feeling of unity, feeling of "WE" consisting of bright "I" is formed more quickly
Each class, being a unit of the educational system, has the right to create intraclassic traditions, to manifest initiative, leadership in general school affairs. In the development of the individuality of each student, the work of class leaders on the diagnosis of pupils and class personnel is of great importance, carrying out a variety of extracurricular activities that allow children to be included in various forms of work, show them on the positive side, and allow them to establish themselves in good works in the team.
Pedagogical support should be mediated by diagnostic results during the class hour, but more often in an individual conversation.
Thus, management should go in the system:

System Management
1. Management of the educational system is carried out flexibly, using three basic forms of making managerial decisions:
1. In the form of co-management - at the highest level of management of such bodies are the school conference. Management decisions are considered to be taken when the agreement is reached by the parties concerned.
2. In the form of self-government, management decisions are taken collectively at the pedagogical councils, the council of the children's parliament, the trade union committee.
3. In the form of administrative management - if the case requires a prompt decision, the director accepts it solely, at the meeting of the administration - collectively.
From the point of view of the scale of the tasks to be solved and the subjects directly controlling, four control levels can be distinguished in the structure of the management system:
1. The level of strategic management - the level of the director.
2. The level of tactical control - the level of the deputy director.
3. The level of operational pedagogical and economic management - the level of leaders of the MO, councils and other bodies.
4. The level of operational student management - the level of teachers, class leaders, students' assets.
The management of the upbringing process is structured as follows (in the following areas)
1. Joint work with the units:
a) Youth Maslikhat;
b) communication with public organizations (schoolchildren's palace, museums, libraries, music schools, etc.)
2. Administrative work:
a) upgrading the skills of class teachers;
b) acquaintance with the experience of the educational work of schools, including the pages of the periodical press;
c) MOs of class teachers;
d) production of methodological materials, bulletins.
3. Information collection:
a) pedagogical observations;
b) questioning;
c) analysis of collected information;
d) graph of the diagrams
.4. Planning:
a) development of programs and plans aimed at the development of students, raising their level of upbringing;
b) the selection of forms and methods in accordance with the collected and developed information.
5. Control and correction:
a) analysis and evaluation of plans and programs of educational work (teachers 'councils, classroom managers' councils, director's reports and other forms);
b) adjusting plans and programs.
6. Creating conditions for the development of the personality of students:
a) a benevolent microclimate in the pedagogical and student groups;
b) the creation of a material and technical base
d) a close relationship between the family and the gymnasium;
e) mutual assistance in conducting extra-curricular, extracurricular, extracurricular activities;
f) work with students' assets;
g) seminar for class leaders;
h) visiting and analyzing extra-curricular activities.
The management system creates opportunities in which the educational process becomes effective and valid. With the interaction of all the components of management, we present the following image of the school and model of the student:
3 Expected image of the school:
- This is a school where the polyvariant components of the educational environment function effectively, namely: ecological, civil-patriotic, legal, moral directions, vocational guidance, the organization of educational and cognitive activities, artistic and aesthetic upbringing, sports-physical direction, self-management and co-management.
- In this school form and develop a personality with a creative beginning and developed intelligence.
- In this school, class leaders work on educational programs, based on a person-oriented approach to the child.
It created the most favorable conditions for mental, moral, emotional and physical development of the individual.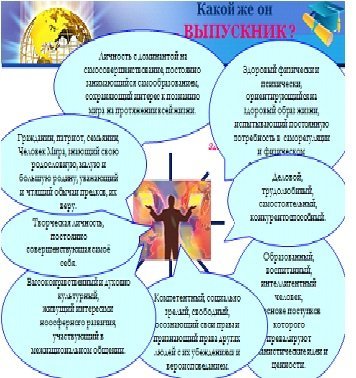
PROGRAM
"From legal knowledge to civil position" Secondaryschool№21
In the modern world, the right to education is regarded as one of the fundamental natural fundamental human rights. This understanding of the right to education is enshrined in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the Convention against Discrimination in Education, the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, the Convention on the Rights of the Child, the European Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms. UNESCO recommends that the right to education be considered as an element of the right to life, the right to development, the right to lifelong education, which must be realized throughout the life of a person.
The child spends most of his childhood as an apprentice. From what experience he will get in school - the experience of a friendly and confidential atmosphere, respect for his rights and human dignity or the experience of studying in an atmosphere of indifference, indifference, cruelty, his success in society largely depends
The social role of students is determined, above all, by their upbringing, and especially by legal education. However, as shown by sociological research,
At present, new value orientations of representatives of the younger generation have appeared, which lead to the commission of offenses.
So, according to the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Republic of Kazakhstan, in January-November 2009, almost every fifteenth (6.6%) crime was committed by minors or with their participation.
On the one hand, 6.6% is an insignificant indicator, if we consider it abstractly. But the fact that 6.6% of the total number of crimes committed in January-November 2009 in Kazakhstan falls on young people of minor age, indicates that these teenagers are already involved in the illegal (criminal) sphere from an early age.
In addition, today's youth are characterized by such negative social deviations, kakalkolizatsiya, tobacco smoking, drug addiction, teenage prostitution, youth extremism. We have to state that such negative manifestations of deviant behavior accompany young people long before their majority.
In these most socially dangerous deviations, the negative attitude of young citizens towards law, law, legal nihilism, and lack of faith in resolving issues in a legal way is clearly manifested.
One of the main reasons for this, in our opinion, is the insufficient level of legal education of young citizens in the family, educational institutions, and other social institutions.
The results of sociological research conducted by us in 2008-2009. in the form of questioning (questioning) of young citizens aged 14-18, showed that just over half of high school students (63.7%) were able to obtain the necessary legal knowledge in the process of schooling. According to the students themselves, 15.8% of them did not receive sufficient knowledge in the field of law. The fifth part (20.5%) of respondents found it difficult to answer the question positively (Fig. 1).
Thus, in school, there is an acute need to create a legal system, beginning with the elementary stage, ending with the senior classes.
The goalof legal education is the formation of a legal culture of the individual.
Tasks:
-
to give knowledge about rights, duties, norms and laws;
-
to introduce students into complex legal relations;
-
to develop skills of conflict-free communication.
Pedagogical position:protection, mediation, self-education and correction of one's own behavior and knowledge.
Age approach to legal education
Younger schoolchildren
Tasks:
1. acquaintance with the rights and duties in their ambivalence;
2. training in respecting the rights of others;
3. familiarization with the rules and norms of behavior in school;
4. the formation of a position of responsible attitude to state property.
Means and methods: fairy tales, situations, game.
Average school age
Tasks:
1. active inclusion in the practice of self-government;
2. training in decision-making skills;
3. formation of the position of a member of the team and responsible attitude to actions;
4 familiarity with the legal basis of the state and laws that protect and limit the rights of children;
5. Introduction to the mechanism for protecting the rights of children in the republic and the world;
6 the formation of the ability to live in a conflict-free space.
Means and methods: plot - role games, debates, discussions, etc.
Senior students
Tasks:
1. active involvement in the practice of self-government and influence on preserving the traditions of the legal space of the school;
2. acquaintance with the basics of the legislation of the republic, protecting the rights of minors;
3. training skills of protection, self-defense;
4. Education of civil liability.
Means and methods: self-management, self-regulation, self-organization; the involvement of everyone in the work of the collective.
Expected results: Creation of a system of civil-patriotic and moral-legal education of pupils, which helps children to understand their belonging to the destiny of their Fatherland, responsibility for themselves and the surrounding reality, readiness and ability to build a life worthy of a person.
PROGRAM OF PATRIOTIC EDUCATION
"PATRIOT" school № 21
|
Name of the program |
Program of patriotic education of schoolchildren
"PATRIOT" school № 21 |
|
Program Executors |
Teachers and students of the State Institution "School №21" |
|
Purpose of the program |
Development of citizenship, patriotism as the most important spiritual, moral and social values among young people, readiness for active manifestation in various spheres of society's life. Formation of a spiritually and physically healthy person, inextricably linking his fate with the future of his native city, region and country. |
|
|
The development of a spiritually-moral personality that intelligently combines personal interests with social interests. Education of a sense of duty, responsibility, readiness to defend the Fatherland, a feeling of love and affection for the family, home, home, traditions, customs of their people. Forming skills and the need to preserve and multiply the riches of nature. The formation of the necessary material and legal standards of conduct in terms of state, labor, civil and family laws, awareness of oneself as part of a state governed by law, capable of cooperating with others through the study of the Convention on the Rights of the Child. Development of moral relationships in the family. Raising pride for the heroic past of their homeland and respect for the culture of their country. |
|
|
2013-2016y. |
|
Tasks of the program |
Spiritual and physical perfection, awareness of rights and duties to the state and society. Formation of a persistent patriotic position. Formation of an integral, scientifically-based picture of the world, familiarization with universal human values. The upbringing of the need for spiritual enrichment. The general development of the personality, the assimilation of the norms of human communication, the sensory perception of the world. Consolidation of efforts of the subjects of the educational system for the development and formation of the individual and individual assistance to the child. Forming an active life position of youth, orienting it towards a healthy lifestyle. Raising the level of social activity, civic responsibility, spirituality of adolescents and young people, raising the status of participants in the event. Forming a positive image of the State Institution "School No. 21" through replicating the innovative experience in civil-patriotic education in the city. |
|
Terms of the program implementation |
|
At present, events in Kazakhstani society are associated with changes in all spheres of our life. The economic transformations, the stratification of society that affected each family, led to a change in the attitudes and values of children and adolescents, their estrangement from the adult world, a negative attitude to the concepts of human dignity, civic duty, personal responsibility. The growing deficit of humanity, social tension, deformation of families adversely affect the moral and physical health of the younger generation. A new type of war has emerged - terrorist wars, from which, first of all, civilians suffer, usually not prepared for extreme situations. Any country needs an effective system of patriotic education. Its content should correspond to the current situation in the country, and its system should be flexible and constantly changing in the light of modern requirements. Researches of scientists have convincingly proved, that education is closely connected with education of patriotism. In connection with this, a program has been developed for the education of children and adolescents, whose goal is social formation, patriotic education, the formation of an active civic position of adolescents in the process of intellectual, spiritual and moral and physical development, preparing them for the defense of the Fatherland, teaching them how to behave properly in extreme situations , be able to help yourself and others. "Education of a citizen of the country should be regarded as one of the main means of national revival. A functionally competent citizen is a person who loves the Motherland, who is able to respond to changes in society, and to defend his human rights. " Developing this program, we proceeded from the specific capabilities of our school. Analyzed the psychological readiness for this work of teachers and students, material and methodical support.
The concept of "Citizenship" presupposes the development and realization by the child of his rights and duties towards himself, his family, the collective, his native land, the Fatherland. These questions are not only philosophical, social, economic, but also purely pedagogical. It is important to educate an active citizen of his country, and not an outside observer. Citizenship includes relations at the level of "citizen-state" and "person-society". When forming a citizen, we must first of all see him as a person. Therefore, the citizen from a pedagogical point of view is an original individuality, a person who has a unity of spiritual, moral and legal duty.
Patriotic education is the systematic and purposeful activity of government bodies and organizations in shaping citizens' high patriotic consciousness, feelings of loyalty to their Fatherland, readiness to fulfill civil duty and constitutional duties to protect the interests of the Motherland.
Patriotic education is aimed at the formation and development of a personality possessing the qualities of a citizen;
Article 2 of the Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan "On Education" defines the requirements for educational activities in state educational institutions.
Among the most important is the task of patriotic orientation: "Education of citizenship, diligence, respect for human rights and freedoms, love for the surrounding nature, Motherland, family."
Today patriotism is identified with such personal qualities as love of the big and small homeland, respect for family traditions, readiness to fulfill the constitutional duty to the Motherland.
In our opinion, it is these personal qualities that are lost in modern society, and the notion of "patriotism" becomes somehow faceless, far from being understood by today's schoolchildren. Therefore, the main task of the teacher is to take care that the child does not lose the feeling of disinterested love for the mother, close people, love for his home, which has been inherent in his soul since birth.
The main thing in the program is a systematic approach to the formation of the student's civic position, creating conditions for his self-knowledge and self-education. It is important to make optimal use of the pedagogical potential of the social environment, to help students learn social and historical experience by entering the social environment, to develop their own individual experience of life.
The program is recommended to use in secondary school from the 1st to the 11th grade. It includes 6 directions linked by the logic of the formation of a citizen of Kazakhstan. The program gives the educator greater freedom of creativity.
Goal:
-
Development of citizenship, patriotism as the most important spiritual, moral and social values among young people, readiness for active manifestation in various spheres of society's life.
-
Formation of a spiritually and physically healthy person, inextricably linking his fate with the future of his native city, region and country.
Tasks:
-
The development of a spiritually-moral personality that intelligently combines personal interests with social interests.
-
Education of a sense of duty, responsibility, readiness to defend the Fatherland, a feeling of love and affection for the family, home, home, traditions, customs of their people. Forming skills and the need to preserve and multiply the riches of nature.
-
Development of moral relationships in the family;
-
Raising pride for the heroic past of their homeland and respect for the culture of their country.
The basic principles of the organization of education:
-
The principle of integrity-semantic equality.
-
The teacher and pupil have a common goal, interesting joint activities, equal views on universal human values, positions of equality. Leading with respect to the adult and the child is the principle: "Although you are also a child, but the same person, like me; I respect you. Together we are doing a common cause. "
-
The principle of continuity and systemic educational impact at all levels of continuous education. Interrelation of the processes of education and training.
-
Conceptual principles of joint education (democratization, humanization, regionalization).
-
Accounting for the patterns of psychophysiological development in each age period, providing a personal-oriented approach to the upbringing of children and adolescents.
-
Principles of organization and self-organization, (student activity, motivation, willingness to cooperate, creativity and communication).
-
The principle of development is the path of the educational system along the following levels: the emergence, becoming, the period of maturity and transformation.
Participants of the program:pupils of 1-11th grades of the State Institution "Secondary General School №21"
Organization of the program
The program is based on the principles of systematic, scientific, accessible, tolerant and is designed for five years. The structure and organization of this educational program is built taking into account the different age categories of students, in connection with the specific features and tasks of the spiritual moral and physical development of students of different school age and takes into account the degree of preparedness of students for life and work in the team, their ability to make decisions and act independently.
I category: guys 1-4-x classes. The process of forming readiness for the defense of the Fatherland, fostering love and respect for the small homeland among younger schoolchildren is built taking into account their limited life experience, the nature and amount of knowledge received, and the overall tasks of education and upbringing. Its effectiveness in this period is determined, first of all, by close connection with the fulfillment of educational, general educational tasks. The educational effect of all forms of patriotic upbringing will depend on how systematically the knowledge of the children about their homeland, the people living side by side, their moral, emotional-strong-willed attitude to the activities for protecting loved ones will be formed. The task is to build on the high emotionality, impressionability and receptivity, develop in the younger school students feelings of admiration for relatives, classmates, people living in our country.
II category:students of grades 5-8. Adolescents have a need to analyze and generalize facts and phenomena of reality, develop their own views on the surrounding, on moral demands and assessments. The most important in the formation of value orientations in adolescents is the participation of schoolchildren: in various types of military-patriotic activity, competitions, competitions organized in the school.
III category:students of 9-11 grades. This is the period of formation of the scientific outlook, intellectual and physical development of man, his professional self-determination. Therefore, the school must prepare students for a conscious choice of a profession, including military. In the educational process, students should not simply transfer knowledge about different professions, about the events in the country, or about its historical development, but also to form their responsibility for its future, to inculcate socially valuable experience of protecting their Motherland
PROGRAM "ROAD TO YOURSELF"
Section 1. GeneralProvisions
The program is aimed at creating conditions for obtaining a high-quality education appropriate to modern ideas, developing erudition, and shaping the need for self-education.
Purpose of the program: Development of abilities and cognitive interests of students.
Expected results: Sustainable scientific views on nature and society; independent and rational thinking; conviction and readiness for self-realization, the ability to navigate in new life circumstances
Section 2. Main directions and their implementation
|
Direction |
Tasks |
Content of activities |
|
Organization of student learning activities |
1. Develop skills to scientifically organize mental work. 2. Formation of responsibility for educational work. |
Conducting of class hours
"Learn - learn."
- Organization of assistance in study. |
|
Individual work with students |
Formation of positive motives for learning. Studying the age and individual characteristics of students. Coordination of activities of subject teachers. |
- Diagnostics "Motives of educational activity"
- Observation
- Involvement of the small pedagogical council, work with parents, information, joint search for solutions and analysis.
- Psychological and pedagogical support |
|
Development of cognitive interests |
Creation of conditions for development of cognitive interests of students.
Creation of a school-wide intellectual club "Erudite" |
- Conducting intellectual games, subject weeks, decades, olympiads ...
- Conducting role-playing games, discussions, contests for developing and developing abilities.
- Development of a plan for the activities of the club and organization of meetings. |
PROGRAM
"HEALTHY LIFESTYLE FROM TEACHER TO STUDENT"
According to the definition of the World Health Organization, "health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being ...".
The concept of "health" reflects the quality of adaptation of the body
to the conditions of the environment and represents the outcome of the process of interaction between man and the environment.
The very state of health is formed as a result of the interaction of external (natural and social) and internal factors (heredity, gender, age).
The main goal of the program is to preserve the health and optimize the personal and professional development of the subjects of the educational process on the basis of the introduction of health-saving principles. Increasing the qualifications of teachers in matters of health culture. This is the main condition for solving the problems of education in the field of health
The modern state of society, the pace of its development, place high demands on the individual and his health. Proceeding from this, the modern school should not only give students a certain amount of knowledge, skills and skills, but also form a person with a high level of self-awareness, thinking, ie, To provide every schoolchild with opportunities to identify and develop abilities, talents and ingenuity with proper protection and strengthening of health.
The experience of some schools shows that the creation of a favorable educational environment contributes to the health of schoolchildren.
The biological reaction of the schoolchildren's organism depends both on its adaptive capabilities and on the strength of the combined impact of the educational environment.
Many parameters of the educational environment are regulated by sanitary
norms and rules that are mandatory and must be implemented in the interests of preserving the health of schoolchildren.That is why the developed program
"Healthy lifestyle from teacher to student "is aimed at the introduction of health-saving technologies and valeological education of students. All the services of the school are involved in the implementation of the program:administration, teachers, teacher-organizer, teacher-psychologist, medical worker.
PURPOSE OF THE PROGRAM:
The purpose of this program is to find the best means of preserving and
strengthening the health of students in schools, creating the most favorable conditions for the formation of schoolchildren's attitudes toward a healthy lifestyle as one of the main ways in achieving success.
PROGRAM OBJECTIVES:
1. To work out a system for determining the level of health of schoolchildren and purposeful tracking of it during the entire training period.
2. Create conditions for ensuring the protection of students' health, their full physical development and the formation of a healthy lifestyle.
3. Popularize the benefits of a healthy lifestyle, expand the horizons of schoolchildren in the field of physical culture and sports.
4. Education of parents in matters of health.
5. Propagation of a healthy lifestyle.
6. Introduction of modern methods of health monitoring.
7. Encouraging students to acquire the knowledge, skills and knowledge necessary to make reasonable decisions to preserve their personal health, and to preserve and improve a safe and healthy environment.
MAIN DIRECTIONS OF THE PROGRAM:
1. Organization of health-saving educational process:
- updating and replenishment of the legal framework of the school;
- Ensuring compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards in the organization educational process, occupational safety and health standards;
- ensuring the health-saving mode of the school;
- organization of a rational nutrition system for students;
- providing the optimal mode of motor activity of students;
- development of a set of measures to identify the level of physical and psychological health of students.
2. Instructive and methodical work with students, their parents and teachers:
- organization of seminars for school teachers;
- the organization of a parent education;
- conferences, lectures, quizzes for students on valeological topics;
- carrying out of briefings on safety precautions, labor protection, fire safety.
3. Educational work:
- use of health-saving technologies during class and after-hours activities;
- development of valeological themes of class hours;
- organization of work of school sports sections;
- organization of the work of circles of valeological orientation.
4. Prevention and correction of health:
- Physical education, gymnastics for the eyes;
- holding days of health at school;
- Carrying out sports and mass events.
PREDICTABLE RESULT:
Healthy physically, mentally, morally, adequately assessing his place and purpose in life is a graduate.
PARTICIPANTS OF THE PROGRAM:
• students;
• class leaders;
• teachers - subject (OBZH, biology, physical education);
• Parents;
• medical workers.
• teacher-organizer;
• Teacher-psychologist;
• school administration
PEDAGOGICAL MEANS:
• a program of teaching subjects that form the basis of a healthy lifestyle; Days of health.
• a package for diagnosing the health status of students.
EXPECTED RESULTS:
• raising the level of physical, mental and social health of children;
• increase the level of preventive work;
• Forming the attitude of children and their parents to their health as a the main factor of success at subsequent stages of life;
PROGRAM "MY CHOICE"
(professional self-determination)
Section 1. General Provisions
Currently, the market creates conditions for freedom of choice of life and professional path, it simultaneously leads to the lack of demand for part of the population, i.e. to unemployment. In this situation, the school's concern about the well-founded choice of a profession by its graduates, the formation of their qualities that will enable them to be in demand become urgent tasks, deciding which the school realizes its humanistic function will help young people to exercise professional and social self-determination. This is possible only in the case when there is a system of vocational guidance work,which is understood as the interaction of the individual and society in providing the social and professional structure. Self-determination is the realization of one's attitude towards the world, the assertion of one's position in it. The choice of profession occupies a very important place in the self-determination of the individual In modern conditions,professional self-determination presupposes choosing a career, the sphere of application and self-development of personal opportunities, as well as the formation of a conscious attitude of the individual to sociocultural and vocational-production conditions.
Labor activity is the most important sphere of self-realization and self-expression of the individual, provides the disclosure of potential opportunities and abilities of the individual. Therefore, in carrying out career guidance work, it is necessary to identify individual psychological qualities of the individual, the level of the formation of social claims, the value-moral orientation.
The choice of the profession is based on the correlation of the abilities, abilities and interests of students with the assessment of the state of social needs in the employees of certain specialties. The basis of professional self-determination is based on the three-factor model of EA Klimov (I want, I can, I must).
When constructing a vocational guidance system for schoolchildren, we adhere to the structure proposed by a group of scientists led by SN Chistyakova, which consists of three elements: the schoolchild acquires knowledge about herself (the image of "I"); information about the world of professions; implementation of professional samples (correlation of knowledge about oneself and knowledge of professional activity).
In the organization of career guidance work, an age approach is necessary: Stage 1 - children's play, in which there is a kind of "fitting" of the professional role; Stage 2 - teenage fantasy; 3 stage, exciting teenage and part of adolescence, - a preliminary choice of profession based on interests, abilities, value system; Stage 4 - practical decision-making. The nature of the content and the amount of work will vary depending on the age of the students, reaching maximum intensity in the pre-graduation and final grades. If in the primary classes vocational guidance practically merges with the labor education, then, as you approach the end of the school, vocational guidance work increases.
Purpose of the program: To promote the actualization of processes and mechanisms for the professional self-determination of students and enrich their knowledge, skills and abilities in choosing a life and professional path
Objectives of the program:
- Formation in schoolchildren of a positive attitude towards themselves, confidence in their abilities in relation to the realization of themselves in the future profession.
- Acquaintance of students with the specifics of professional activity and new forms of labor organization in the market conditions.
- Involving parents in the program
Expected results:
- Students should understand the role of labor in the life of each person and their own.
- Have an idea of the world of professional work.
- Students should be able to self-determine, taking into account their abilities, interests and opportunities, at the exit from the school.
PROGRAM
"FAMILY AND SCHOOL TOGETHER"
«FAST- Family and school together»
Section 1. General Provisions
The interaction of teachers with the parents of the student should be aimed at creating a single educational field, a unified social sphere where the highest values are the basis of a life worthy of a person. The family fulfills a formative role in the formation of the child's personality, which depends on the value orientations of its members. The teacher should have information about what relationships in the family and how they can affect the child's personal development, his character, behavioral reactions and taking into account this, choose the directions and forms of work.
Purpose of the program: Establishment of close contact with parents, involvement of parents in active participation in the organization of teaching and educational process and school management.
Successful solution of the tasks of upbringing is possible only if the family and the school cooperate. The cooperation between the family and the school becomes more and more relevant and in demand. Both sides present their own, sometimes just claims. So teachers complain about parents' lack of interest in the school life of their children, at times poor upbringing, lack of moral values, passivity. Parents, in turn, are unhappy with the excessive workload, the indifference of the teacher, the relationships in the children's team.
In the period of reforms, the education system is changing so rapidly that parents often do not have a sufficient understanding of these changes, focusing in educational activities mainly on their school experience, which often lags behind modern requirements. To address this discrepancy, the educator needs to make the educational process as open, informed and accessible to the parents as possible. The practice of the school shows that parents begin to strive for active cooperation with the school and the teacher, if mutual understanding arises between them. And it is born in a joint activity. Hence, the teacher must take care to become the organizer of a vital program of interaction between the family and the school.
The main role of parents, put forward at the forefront, is "partnership" with the school. That is, partner parents share with the school not only responsibility for their children, for the result of the educational process and the quality of educational services, but also the authorities, participating in the development of the school strategy, its implementation and monitoring of the achieved results. Partnership is one of the conditions for the formation of the state-public system of education management, which is now recorded as one of the goals of the development of education for 2010-2020. In order for the school today to meet the requirements of society, it must enter into dialogue with society, become a truly open system.
The tools of interaction between the school and our parents are new forms. For the second year in the framework of the NCMED's experiment, we are writing an open report using the "Parents and pupils needs assessments in information about the education system" technology available on the school's website and introducing it at the parent conference. In May 2011, , 9.11 classes. The wishes of the parents were taken into account when planning the school's work in the 2011-2012 school year.
So one of the new forms of interaction between family and school was the "pilot" international project "FAST-Family and School Together", prepared by Mrs. Lynn McDonald's, Ph.D., a professor of social work based on scientific research in clinical psychology at the University of Wiscansin-Madison in Higher School of Social Work (UK).
FAST is a program aimed at strengthening the family, entailing a process of change. The FAST program will change how "professionals" relate and work with families; it will change the way families treat and interact with schools and other social services; it will change the attitude of families towards themselves, and how they interact with each other; and, finally, it will change the way different organizations work together. That is, there will be many changes, and we all know that changing something is not easy. But there is a well-known proverb that says: "If you do what you have always done, then you will receive what you have always received." Therefore, if there is room for improvement, then the changes must occur, and the FAST program is a pleasant, friendly and efficient process that allows to slightly facilitate the process of change.
Russell Berkeley published a book about disobedient children, focusing on attention deficit disorder, children's hyperactivity disorder, and their management. Barkley recommends that, before attempting to change the behavior of children in a structured manner, parents should conduct special, non-directional games with their children for 20 minutes a day. He believes that this strengthens the parent-child couple a positive effect, which is necessary if holding time with the parent or the approval of the parents will be used as a reward.
Our role is to support parents to help them succeed with their children. Strengthening the parental position in their own families. All instructions are first given to parents who, in turn, must bring them to the children.
The ultimate goal of this project is to increase the likelihood of a child's success at home, in school and in society by:
- building up protective factors for the child support parents and strengthen the parent position increased participation of parents in school affairs, strengthening of social relationships with other parents in school and teachers reducing the risk of day-to-day stress for the child and family reducing the risk of abuse of alcohol, drugs and other psychoactive substances (SAS) for the child and family reducing the risk of family conflicts.
The project is designed for different age categories from 5 to 13 years. In our school the project is tested with students and parents of primary school.
The results of the implementation of this program were the following:
· Strengthening the parental position (parents become employees, allies)
· Positive dynamics in training (dynamics in the quality of knowledge, victories in intellectual and creative competitions)
· Joint classroom hours, creative labs
· Monthly meetings of parents and children allow solving jointly arising issues and determining prospects
· Active participation of parents both in classroom and in school activities
· Increased motivation to learn.
· The emergence of class traditions
This program - the "Family and School" innovation - inspires parents to believe in their own strength in multifamily groups held after school, building relationships among parents and between families and school, strengthening the parent-child relationship and strengthening family cohesion.
PROGRAM
CHILDREN'S ORGANIZATION
"CENTER OF CHILDHOOD"
The changing social and political environment has a great influence on the formation of the child's personality. The educational system of the school must take into account the main thing - the person who is able to make decisions, first of all before himself. In this regard, self-government in the school should, above all, be self-management. The self-management program should create conditions for the self-development of a person as a subject of activity, as a person and individuality. Achieve the manifestation of each child in the activities of the school can be, breaking the children into groups according to their abilities, desires and opportunities. Under the guidance of teachers, children should be oriented to eternal absolute values - man, family, fatherland, work, knowledge, culture, peace, land. The development of self-government in the school is the basis for its democratization.
The purpose of the program:To create conditions for the development of the individual creative abilities of the child's personality, the formation of a person with high self-awareness, who has an active morality.
Tasks:
- Creation of a system of self-management as an educational environment of the school, which ensures the socialization of each child.
- Organization of all kinds of collective, group and individual activities.
- Development and strengthening of the bodies of student self-government, involving students in active participation in the life of the school collective.
Expected results: Ожидаемыерезультаты:Students should learn to live in a team, become more active, more united, more united, show initiative, must feel a sense of responsibility for the task entrusted.
This program is aimed at successful adaptation of children in school; disclosure of abilities and inclinations of each child after-hour activity; on the involvement of parents of students in the process of forming a collective and determining the prospects for its development. Also the program is oriented:
· The formation of a culture of communication between schoolchildren and comrades, parents, teachers;
· On the formation of their moral self-awareness and responsibility;
· Learning a culture of behavior based on self-management;
· Formation of moral positions
· Development of self-awareness and culture of self-education.
The program is based on the moral development of the personality, the formation of values of the concepts of "good", "kindness", "consciousness", "responsibility", "collective", "respect", "trust", "empathy," "compassion, and interpersonal relations, a conscious and responsible attitude to learning activity, discipline, charged with business. The entire system of work is built on universal values and is aimed at stimulating the development of the individual.
To achieve the targets, the following tasks:are defined:
· Development of cognitive activity and interests of students' personalities;
· Creation of conditions for self-expression and self-realization of students;
Formation of a conscious attitude towards learning activity.
· Creation of a morally and emotionally supportive environment for the formation of a children's collective and the development of the personality of students in it;
· Increasing the role of student self-government in planning, organizing and analyzing vital functions;
· Attraction of students to the culture, traditions, history of the school, village, ulus, fatherland, using the cultural and educational environment;
· Development of the best human qualities of children in the process of organizing the collective creative activity of the organization;
Formation of civil-patriotic feelings of pupils, feelings of belonging to the fate of the fatherland.
· The program is based on the following principles of humanistic pedagogy:
· Recognition of the identity of each child as the highest social value;
• Respect for the individuality, uniqueness and identity of each child;
• respectful relationships between adults and children;
· Creating a situation of success.
CONTENT OF THE PROGRAM
The program consists of eight sections, each of which involves activities in the following main areas:
· HEALTH
· STUDYING
· MERCY
· CULTURE
· LABOR
· RIGHT
SECTION "IN THE WORLD OF KNOWLEDGE"
Purpose: To form a positive attitude towards teaching, development of cognitive activity, intellectual development of the child's personality.
The content of the work:
· Operation "Live, Book"
· Subject weeks;
· Competition "Visiting the Queen of Sciences";
• intellectual games "Literary Salon", "The World around";
SECTION " A SOUND MIND IN A SOUND BODY"
Goal: Strengthening the health of children and adolescents, physical improvement and athletic training.
The content of the work:
· Conversations on the promotion of healthy lifestyle;
Meeting with representatives of health;
· Competitions of drawings on a sports theme;
· sport competitions;
· Actions against drug addiction, smoking, alcoholism;
· Day of struggle with "AIDS"
SECTION "MY MOTHERLAND"
The goal: the formation of a growing generation of love for the motherland, careful attitude to the people's memory, respect for the country's historical past; the upbringing of patriotism in children, the formation of a civic position.
The content of the work:
· Dances of different nations;
· Holidays;
· Exhibitions of applied creativity;
· Search work for the school museum;
· Military field gathering;
· Review of the song and building;
· Thematic competitions dedicated to the day of the defender of the fatherland;
· Meeting of generations;
· Law week «I am a citizen»
SECTION "CARE"
The goal: the participation of children and adolescents in socially significant activities, the development of moral qualities.
The content of the work:
eeting with veterans of the Great Patriotic War, rear and labor;
· Volunteer work;
· Assistance to veterans of war and labor, elderly people
· Marching above the primary classes, etc.
SECTION "MY NATIVE SCHOOL "
Purpose: to educate students on the best traditions of the native school, the history of the school; the formation of attitudes towards school, as a home, where everyone reveals his abilities, talents and acquires friends.
The content of the work:
· Studying the history of your school;
· Search work on collecting materials for the jubilee of the school;
· Design of stands about the school
SECTION "HOW WONDERFUL THE WORLD IS"
Purpose: To develop in children a sense of beauty: to see, feel, understand beauty and protect it, the formation of aesthetic taste.
The content of the work:
· KTD on environmental issues;
· Thematic competitions of drawings and posters;
SECTION "MY RIGHTS AND DUTIES"
The goal: the formation of students sense of duty, the development of responsibility, a real understanding of life, the ability to adapt in this life.
The content of the work:
· Active participation in student self-government;
· Creation of a network of research societies, clubs by interests
· Carrying out a variety of cognitive affairs together with adults (olympiads, sports days, competitions, shows, debates)
· Protection of creative works
· Familiarization of students with the "Declaration on the Rights of the Child"
· Registration of the corner "Your rights and duties";
SECTION "SCHOOL AND PARENTS"
Aim: pedagogical education of parents; involvement of parents in the educational process; the formation of mutual trust and a positive attitude.
The content of the work:
· Work with the parent committee;
• Competitions "We are a reading family"; "Together-friendly family"
· Sports relay race "Mom, Dad, I'm a sports family";
· Parental Readings;
· Parental education;
· Parent conference "Professions, which are chosen by our children"
Expected result
Adolescent awareness of their importance, the understanding that he does something better than others, that he has an inner power that can lead to the desired result. Recognition of his authority among peers and adults, development of communication skills, active participation in the affairs of the team.
Self-assertion of the individual in the team, the opportunity for a particular child to freely express their views, defend their interests.
Mastering the active style of communication; deepen the processes of self-disclosure; improving the skills of understanding the surrounding people, their inner world; securing the trusting style of communication.
PROGRAM
DEVELOPMENT OF ADDITIONAL EDUCATION
Section 1. General Provisions
Additional education is one of the opportunities for the harmonious inclusion of a person in social activities with an orientation to their own choice of creative work.
Additional education is an independent and valuable form of education that can compensate and supplement what the school objectively can not provide to every child.
Additional education is represented by diverse circles and sports sections, electives.
Section 2. Aims and objectives of the program
The purpose: to provide the legal and regulatory conditions for the implementation of additional education for educational programs to fully meet the needs of students in accordance with the law of the Republic of Kazakhstan "On Education".
Tasks:
- creation of the regulatory and legal framework for the development of the system of additional education;
- change the content of additional education in accordance with the requests of students;
- Increase the level of professional skills of teachers of additional education;
- realization of wide possibilities of additional education in solving the problem of socialization;
- the formation of a pedagogical collective capable of educating children through their interests on the principle of a creative union;
- improvement of structural units of additional education, programs of activities of clubs, clubs;
Section 3. Concepts of additional education
The main goal of the school is to educate a creative person who will have to live and work in conditions of full self-financing and self-financing of the economy, market relations, democratization and self-government, wide publicity.
The problem is that modern education develops only one side in children - performing abilities, and the more complex and important side - the creative abilities of a person - is given to the will of the case and the majority remains at a deplorable level.
The goal of our project is the formation of complex abilities for self-identification, self-realization, self-development.
The concept is based on the ideas of a person-centered education, modern approaches to the formation of creative individuality of schoolchildren in educational and cognitive activities.
1. The idea of priority landmarks.
Priorities serve as priority guidelines for improving the system of supplementary education:
- development;
- morality;
- Creativity;
- culture;
- openness;
- free choice and responsibility;
- socialization.
Orientation to the priority of development implies the creation of the necessary conditions for the development of the personality of the pupil; teacher, and also the pedagogical system; educational complexes and institutions of additional education in general. The main meaning of the pedagogical process is the development of the personality of the pupil.
Orientation to the priority of morality. Realization of this priority presupposes the formation of moral-value orientations of the individual, the development of her moral and creative attitude to reality is the dominant of the programs being implemented, of all the activities of pupils, teachers, and the educational environment.
Orientation to the priority of creativity means that creativity is considered as a universal mechanism of personality development, ensuring its entry into the world of culture, and the formation of a way of existence in the modern world. To implement this priority, an atmosphere is created that stimulates all subjects of the educational process to creativity.
Orientation to the priority of culture means the formation of a common culture, the development of the individual's ability to comprehend aesthetic values, to aesthetic education and experience, to creativity according to the laws of beauty, to the creation of aesthetic values in art and beyond, in cognitive and labor activity, life, behavior and behavior, human relationships. The result of this orientation are the aesthetic value and aesthetic-creative abilities of pupils.
Orientation to the priority of openness is an internal emancipation of additional education, subjects of the educational process.
Orientation to the priority of free choice and responsibility represents the pupil and the teacher the choice of an educational route (program) for content, methodology, experience, pace, complexity, etc. to satisfy their interests, needs, abilities development, creative self-realization.
Orientation to the priority of socialization presupposes the creation of the necessary conditions for the adaptation of children, adolescents and young people to life in modern society and in the context of values, norms, attitudes and behaviors inherent in Russian and world society.
2. The idea of personal orientation
In the center of educational processes in the system of additional education are not programs, and the child himself is the highest goal and the meaning of pedagogical care. It is his interests and individual inclinations, originality of character, personal dignity, the formation of creative individuality that are subject to careful study, accounting and development.
3. The idea of semifunctionality
The system of additional education implements a number of functions:
- satisfaction of educational needs of pupils, their parents, teachers;
- formation of individual achievements in each pupil, success in realizing one's abilities;
- search for new forms of cooperation between adults and children;
- methodical support of the educational process.
4. The idea of cooperation
The implementation of this idea implies joint development activities at the levels:
- "foster child - foster child" - joint creativity;
- "teacher - pupil" - joint development activity, reinforced by mutual understanding;
- "teacher-educator" - joint pedagogical search, exchange of experience, cooperation.
5. The idea of autonomy
Additional education is "this is an independent and self-valuable education".
Realization of the idea of autonomy allows each educational institution, a complex, the collective to show independence in choosing a strategy for its development, goals, content, organization and methods of work.
6. The idea of self-worth of a person
Assumes:
- Attitude towards the individual, her inner freedom as the main value of the education system;
- a call for the uniqueness and uniqueness of the personality of each subject of the educational process;
- Respect for dignity.